New star formation should occur near the core of galaxies and it does.
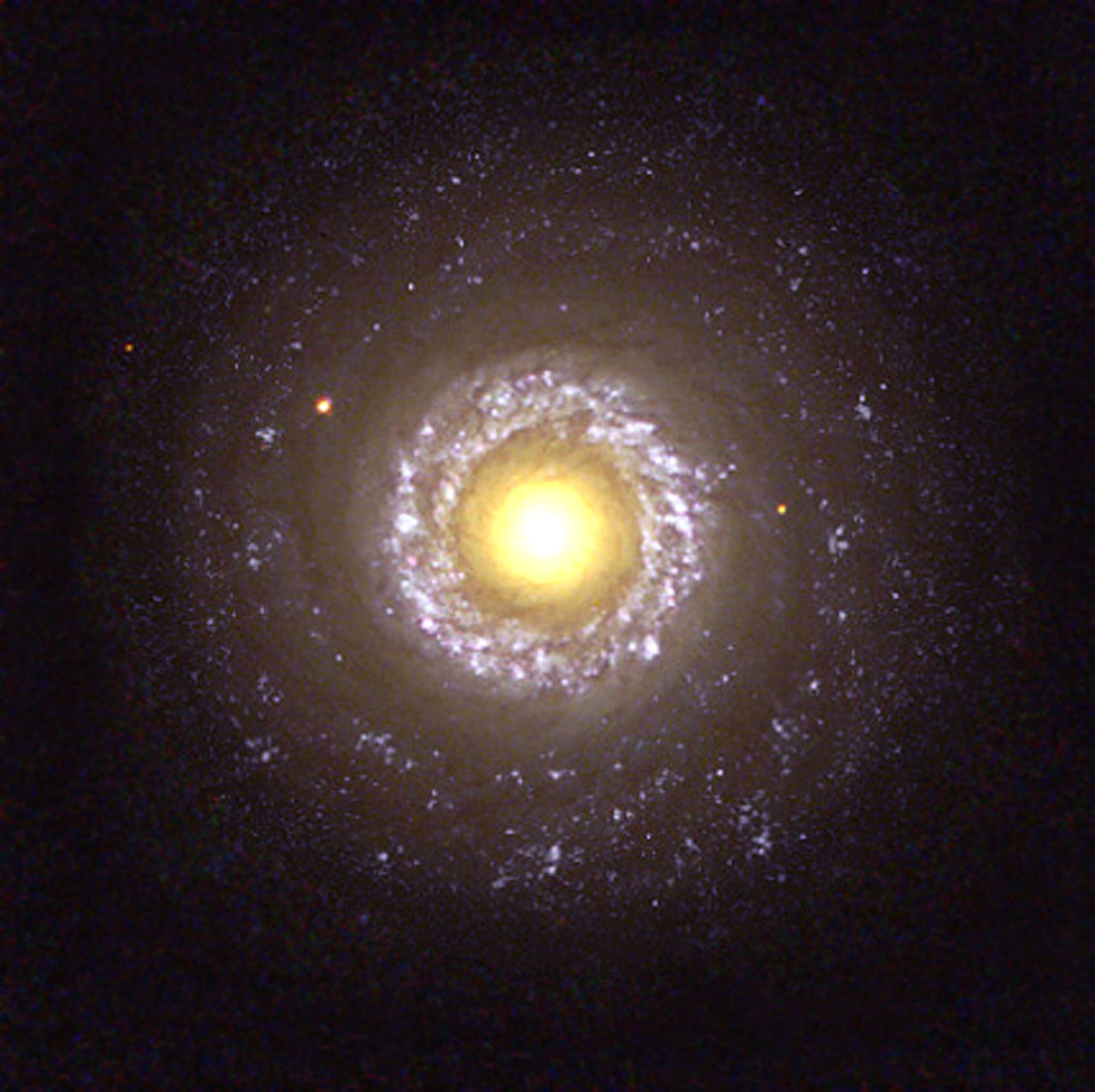

Hydrogen protoplasm should permeate beyond the star forming region of galaxies and it does.
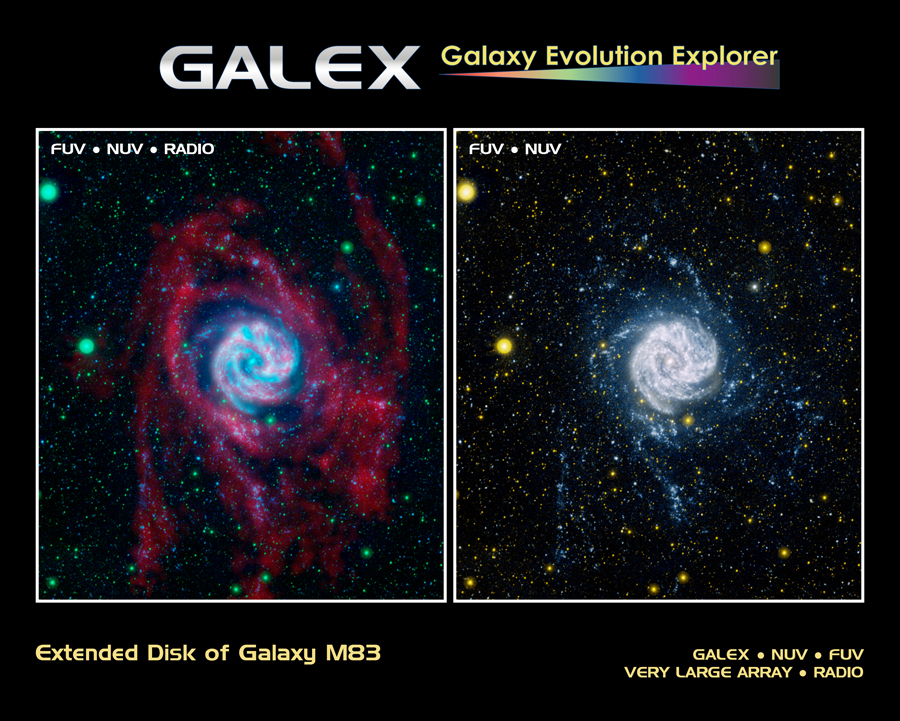
On occasion, neighboring galaxies on a collision course should exhibit the opposite parity of matter and reveal that matter and antimatter repel each other due to opposite gravitational forces and they do.

Newborn stars should concentrate together in clusters around black holes and they do.

As star clusters age the stars should travel away from each other and they do.

Groups of sibling galaxies should appear to be expanding away from a central parent galaxy and they do.
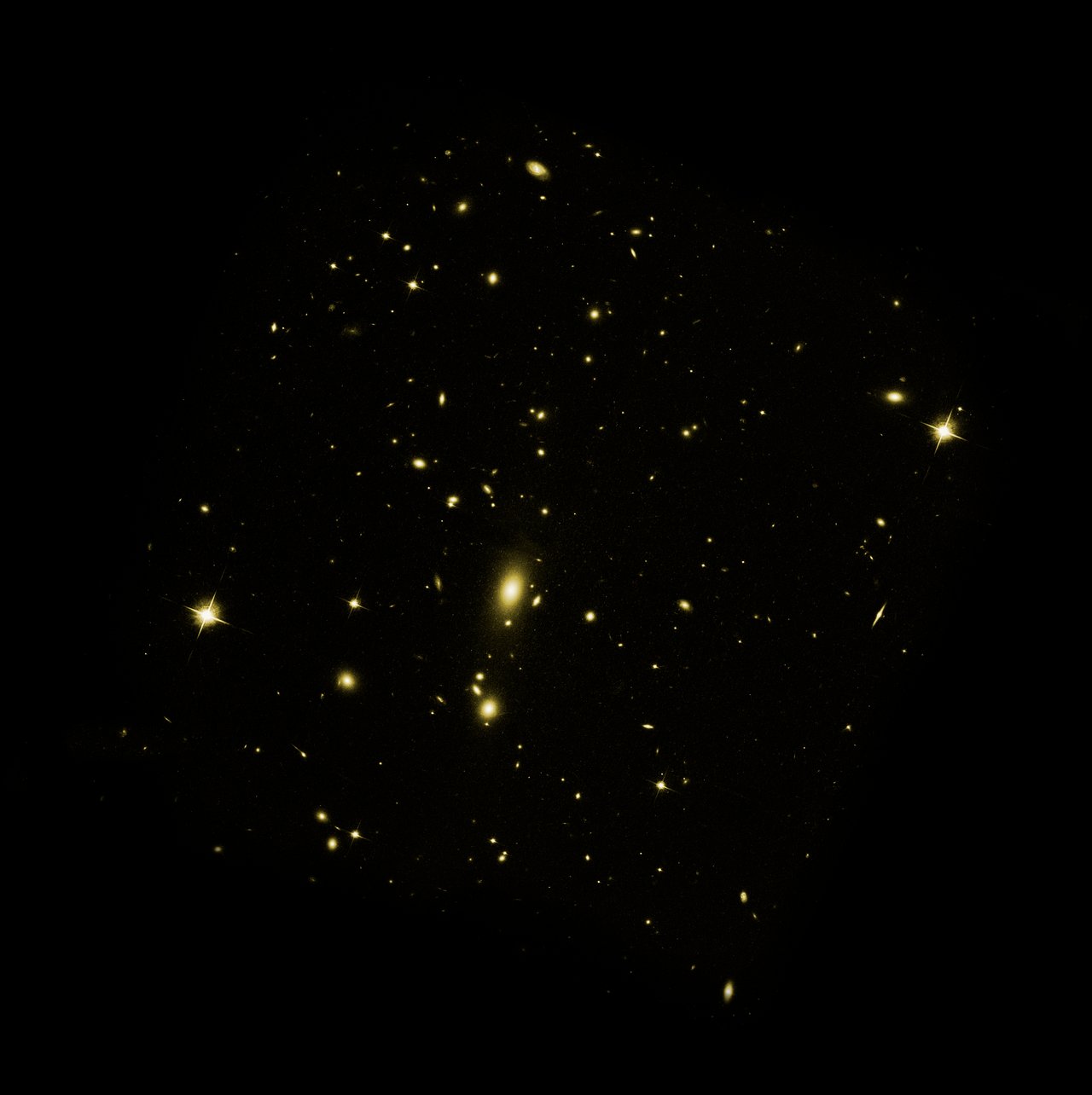

When a model agrees with reality, then a whole host of details reveal themselves to investigators equipped with the proper insight. Evidence lies in discovering galaxies in every stage of evolution, and more evidence remains to be discovered in areas of antimatter and black holes.









No comments:
Post a Comment