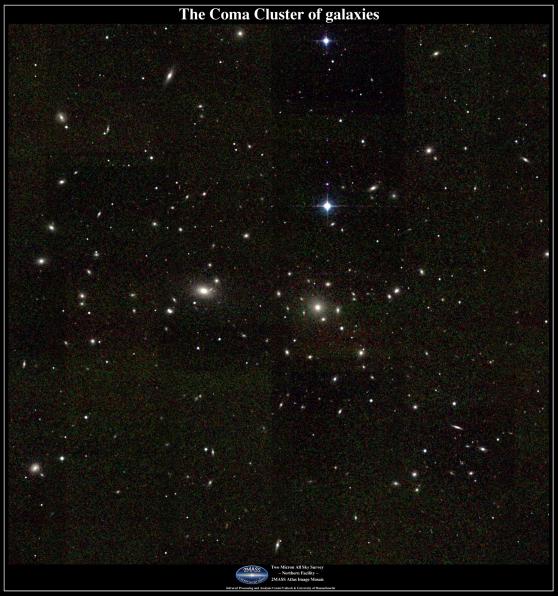
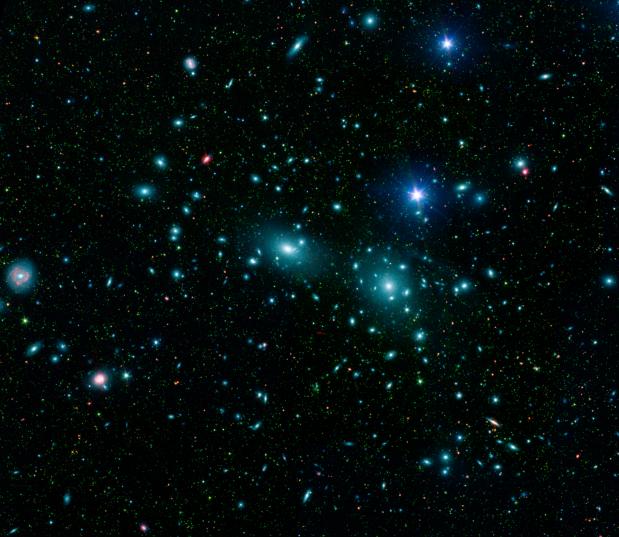
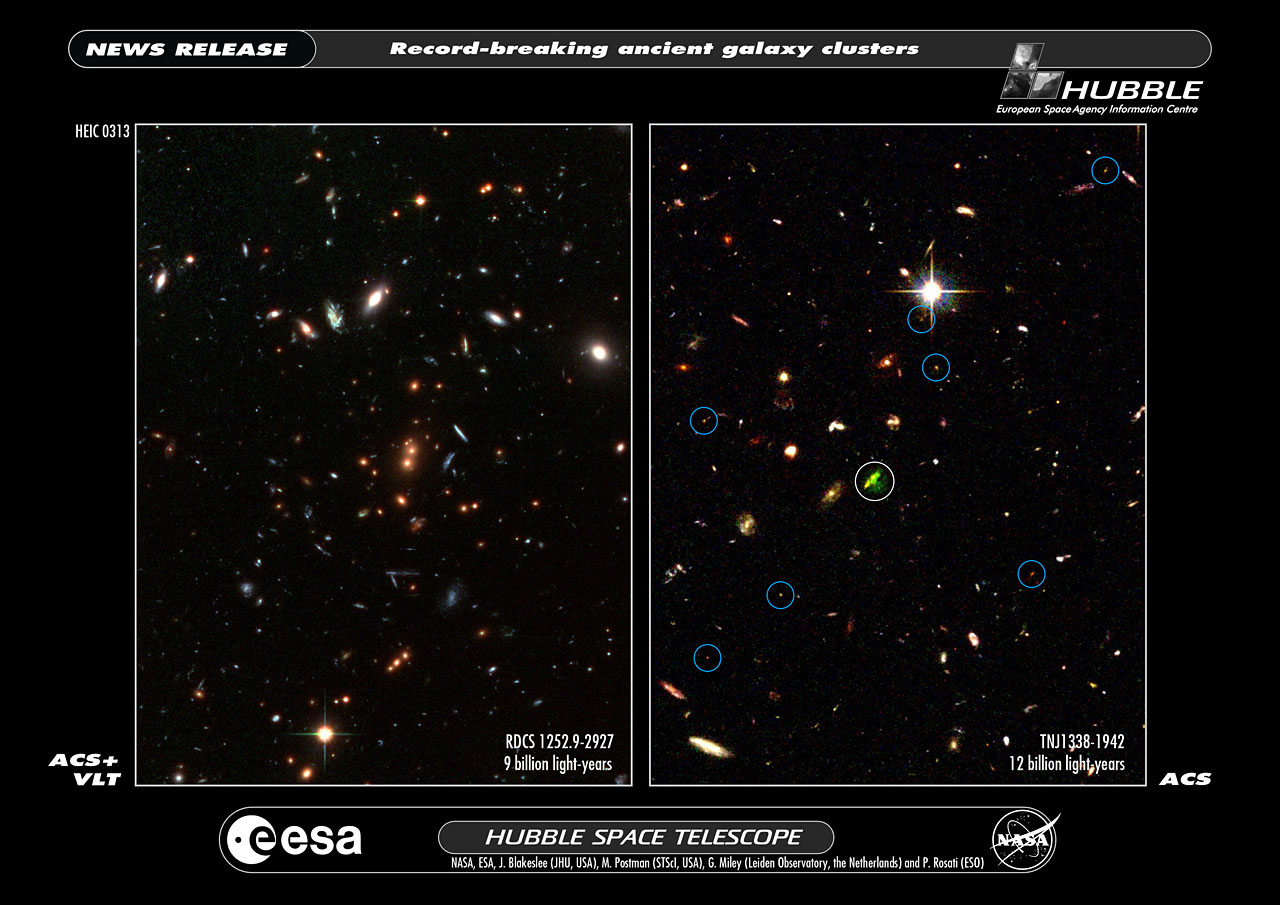
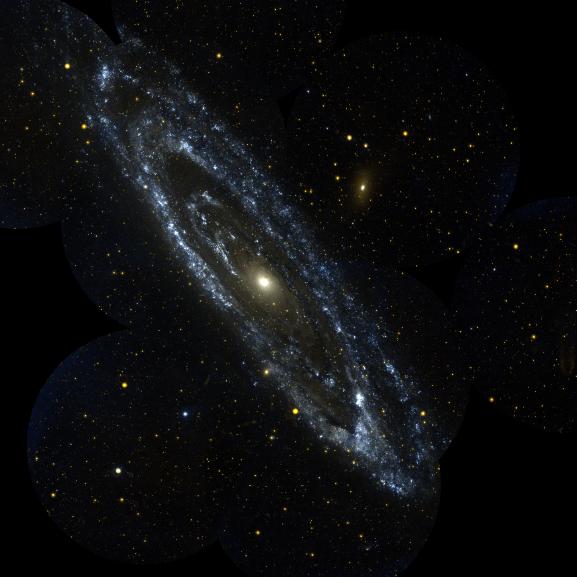
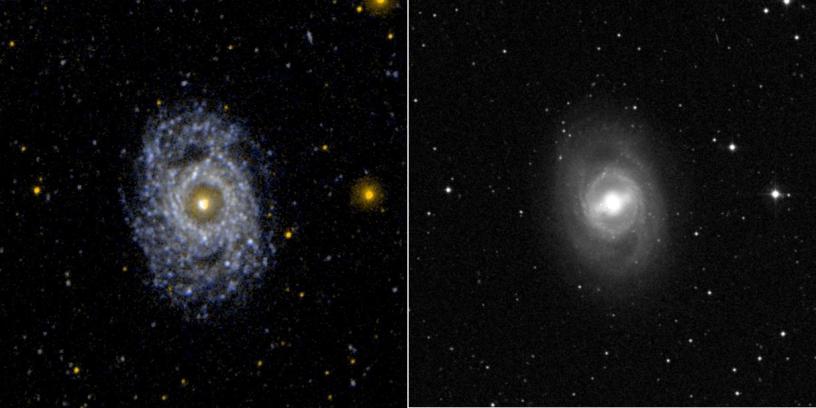
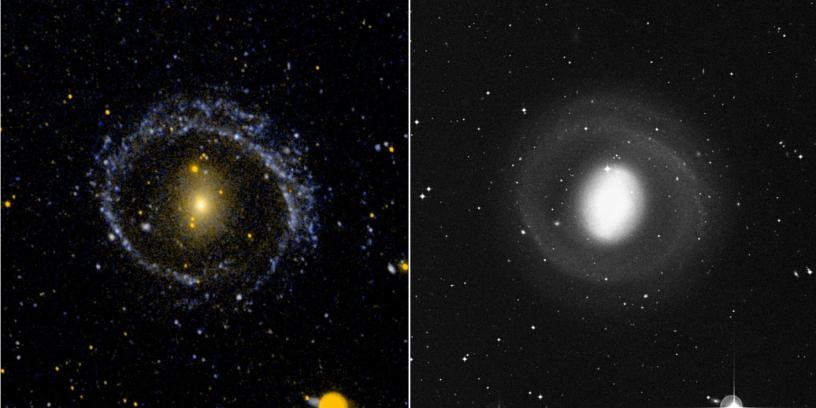
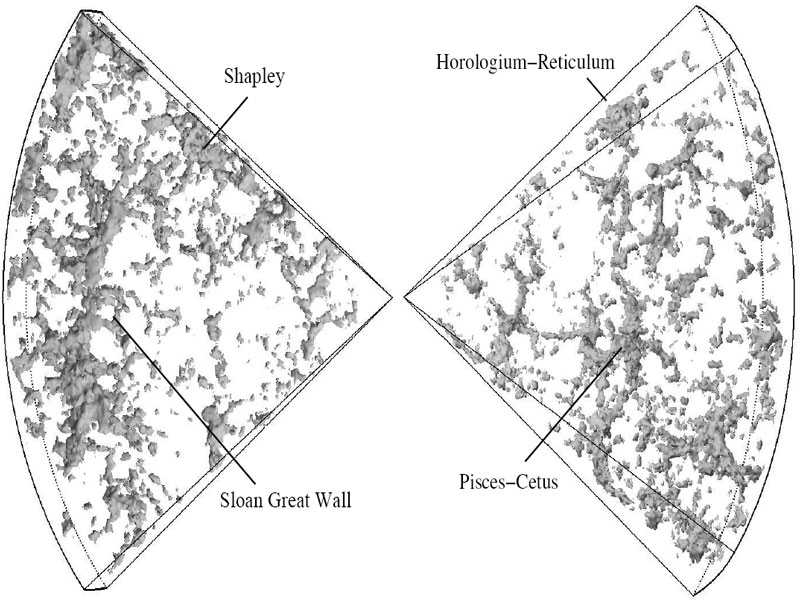
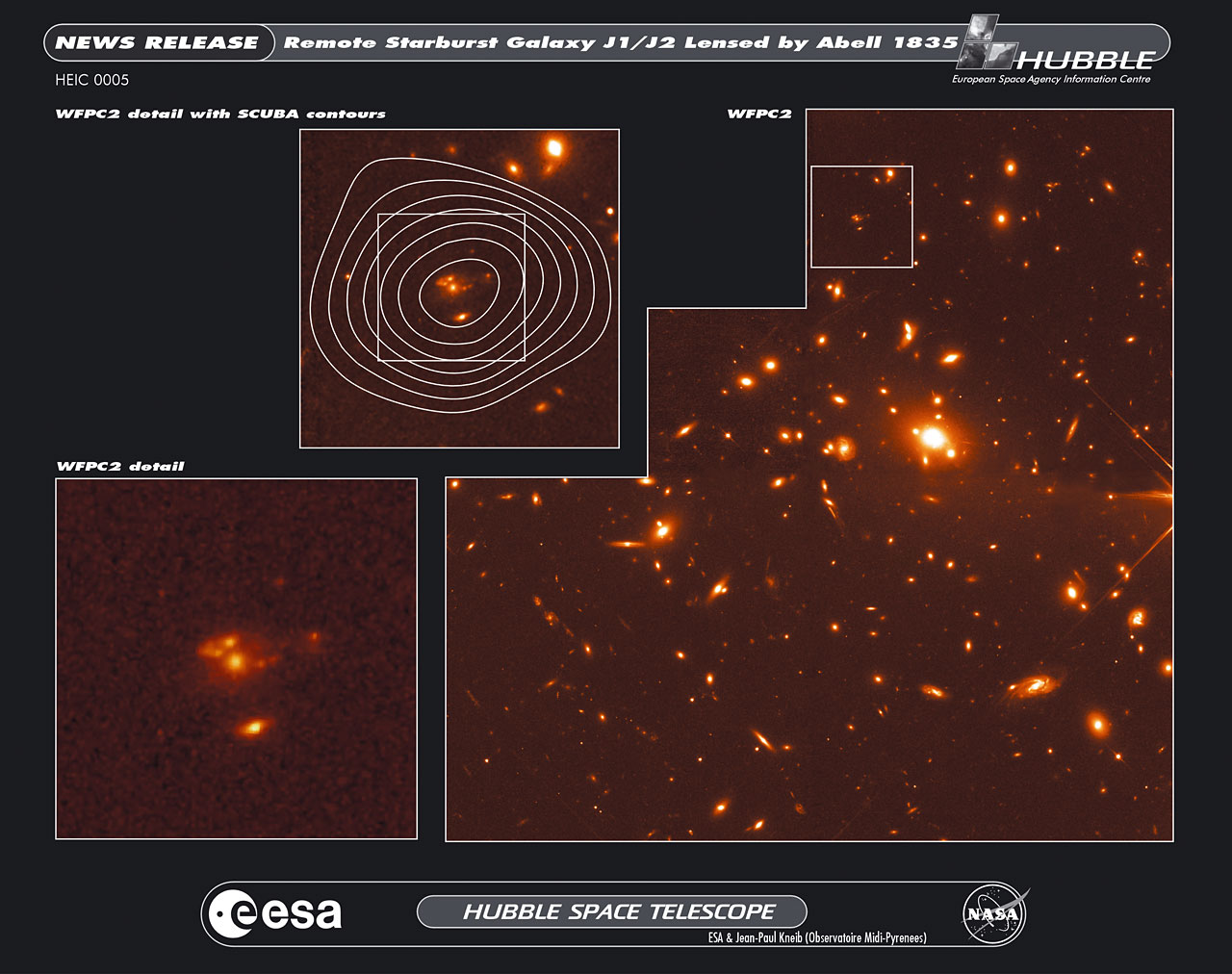
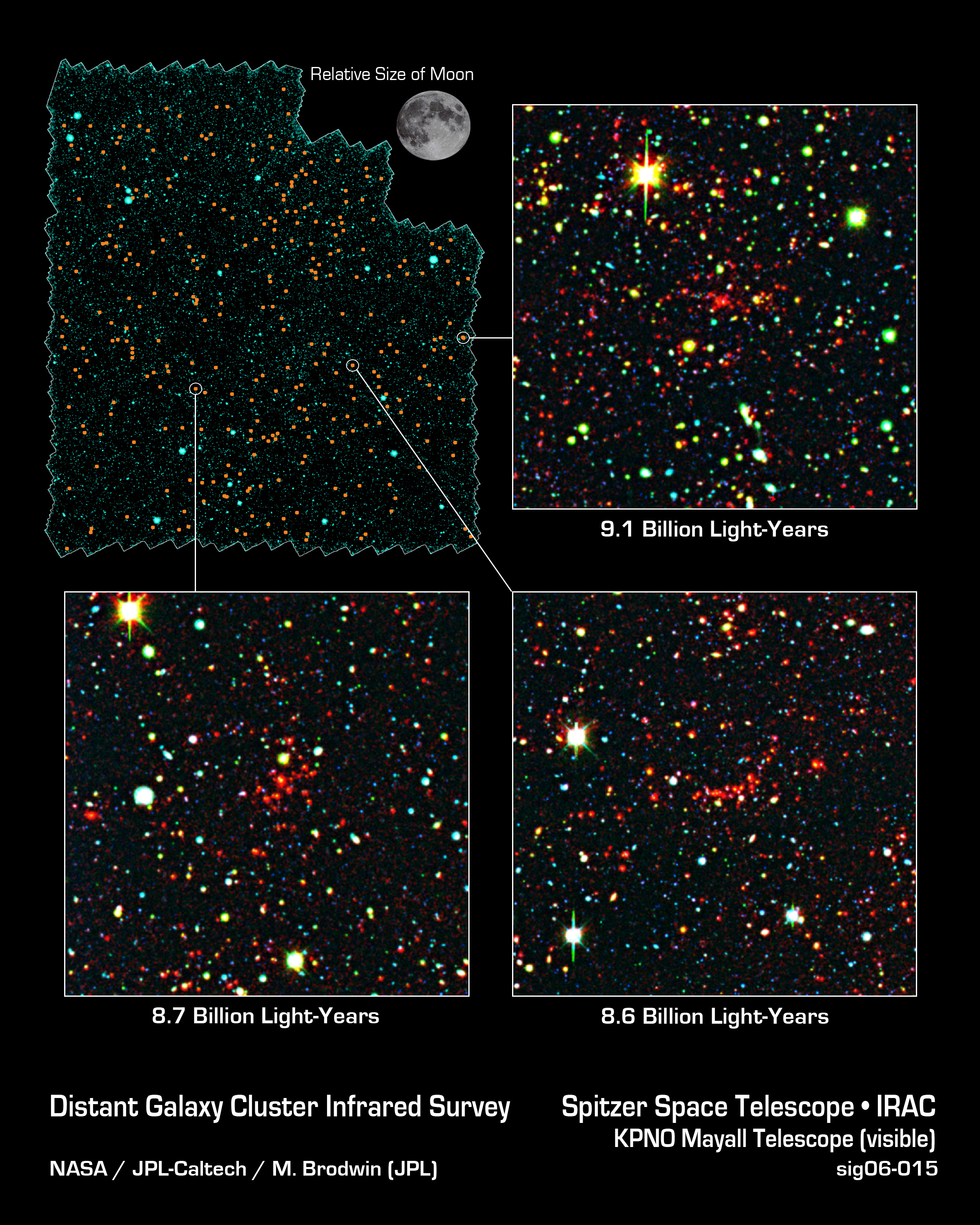
Science operates like a single party political system. Rarely do we find two, rival, scientific factions sustaining a two party system. When factions compete, one faction dominates the other into submission; winner take all. Voting, in the scientific sense, amounts to rallying supporters to adopt one party line over all competitors. It takes a revolution to overthrow the existing order, and defeat is final. Name one discredited scientific theory that has ever regained preeminence. It doesn’t happen. So how would the antigravity hypothesis fare against the incumbent cosmological models of the Big Bang and outside-in galaxy formation?
As a second party candidate, the antigravity hypothesis is officially denied access to the ballot. This is regrettably true. The equivalent of campaigns and elections in the scientific community is peer review publications. The antigravity hypothesis is theoretical speculation, a flight of fantasy based upon circumstantial evidence. As such, it is automatically disqualified from the scientific peer review process. Science fiction is far more tolerant than science fact.
Intelligent design, or creation science or creationism, all faced the same obstacle. Instead of engaging in the formal scientific peer review process, divine intervention proponents formed their own peer review publications, but is that legitimate? Is going outside the system to change the system a credible alternative, or simply self delusional? When speculation cannot get a fair hearing within the conventional peer review process, is it valid to change peers?
Conservative talk radio has arisen as a peer review alternative to conventional media. Christians and Muslims are peer review alternatives to Judaism. Advertising promotes a consumer peer review alternative to competitors’ products. And conspiracy theorists promote a peer review alternative to establishment views. Any peer review process needs to expose two faults: delusion and fraud. Danger lies in peer review alternatives that ban or ridicule dissent.
Mortgage Crisis Solution
11 years ago